| |
|
|
| |
Load
Cells
|
Working
|
Load cells works
like calibrated spring. It used for measuring
forces or for weighing system. It converts
force or weight into electrical signal.
A load cell usually consists of four strain
gauges in a Wheatstone bridge configuration.
Load cells of one or two strain gauges are
also available. The gages are developed
from an ultra-thin heat-treated metallic
coil and are chemically bonded to a thin
dielectric layer. "Gage patches" are then
mounted to the strain element with specially
formulated adhesives. The precise positioning
of the gage, the mounting procedure, and
the materials used all have a measurable
effect on overall performance of the load
cell. Wheatstone bridge with strain gauges
that measure this mechanical flexion hence
giving a proportional electrical signal.
This electrical signal is amplified by instrumentation
amplifier because electrical signal output
is very low. Load cells are used for sensing
large, static or slowly varying forces with
little deflection.
|
| |
Load cell
types
|
| • Double
ended shear beam
• Single ended shear beam
• Single column
• Multi column
• Membrane
• Torsion ring
• Bending ring
• Pancake
• Digital Electromotive Force
|
| |
Strain
gauge load cell
|
Strain gauge
load cell consist of a structure that elastically
deformed when subjected to a force and Strain
gauge network produces an electrical signal
proportion to deformation. Example of this
type of load cells are: Beam type load cell,
Ring type load cell.
|
Beam type load cell |
Beam type load cell are commonly employed for low level loads. Four strain gauge, two on the top surface and two on the bottom surface is used as elastic member for a load cell. The range and sensitivity of this beam type load cells depends upon the shape of the cross section, location of point of application of the load and fatigue strength of the material from which beam type load cell is fabricated. |
Ring type load cell |
Ring type load cell has a ring as elastic material. The ring element can be designed to cover a very wide range of loads by varying diameter D, thickness T or the depth of the ring. The load P is directly proportional to the output voltage Eo. The range of ring type load cell controlled by the strength of material used in fabricating the ring. |
|
Styles
of load cells |
| |
Compression/Tension Load
Cells
Compression/tension load cells can be used
for applications where the load may go from
tension to compression and vice versa. They
are ideal for space restricted environments.
|
S-Beam Load Cells
S-Beam load cells get their name from their
S shape. S-Beam load cells can provide an
output in under tension or compression.
Applications include tank level, hoppers
and truck scales.
|
Bending Beam Load Cells
Used in multiple load cell applications,
tank weighing and industrial process control.
Used in multiple load cell applications,
tank weighing and industrial process control.
|
Platform and Single Point
Load Cells
Platform and single point load cells are
used to commercial and industrial weighing
systems. They provide accurate readings
regardless of the position of the load on
the platform.
|
| |
What are
the factors to select a load cell?
|
• Capacity (kgs, pounds)
• Basic type and mode of operation
• Performance or accuracy level -related
to system requirements.
• Method of mounting.
• Approval requirements (metrological,
safety, environmental)
• Material of construction.
• Cost.
|
| |
Repeatability
|
Repeatability is the agreement
between the results of successive measurements
of the load cell output for repeated applications
of a given force applied in the same direction.
Repeatability is normally measured by applying
the full rated load to the load cell three
times under carefully controlled conditions.
Environmental conditions must remain constant
during the test. The measurements are carried
out at the full rated load of the load cell
so the rated output is the average of the
three output values obtained from the test.
Output values can be expressed as millivolts
per volt (mV/V) or millivolts (mV) providing
they are all in the same units.
|
| |
What type
of errors occurred in load cell outputs?
|
Non-linearity, hysteresis
and creep errors are most commonly considered
errors in load cell application.
|
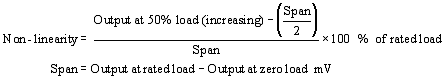
Non linearity
If measurements are being made in one direction
only the non-linearity describes how they
reliance upon a linear output, which is
normally assumed for scaling on amplifier
or meter, can lead to the linearity error
being applied to the measurement point over
the entire range of the load cell.
|
Hysteresis
Our hysteresis data is achieved by using
the mid load point as the reference point
to calculate hysteresis during an incremental
and decremental calibration of the load
cell.

|
Creep: Creep is the
change in load cell output that occurs with
time when a constant load is applied with
environmental and other variables remaining
constant. Creep is specified over a fixed
time period, often 20 minutes.

|
| |
How Environmental
factors affect the load cells?
|
Temperature
Generally temperature changes will result
in a change in a load cell's physical dimensions,
shift in the zero balance of the bridge
and a small change in the Young's modulus
or stiffness of the structure of the load
cell causing an output span change.
|
Pressure
For particular types of load cell, static
or dynamic ambient pressure changes can
cause error due to a net resultant force
exerted on a sensitive form area. |
| |
Load cell
calibration
|
Load cell calibrated by using
one of the three methods.
• Dead weight
• Lever
• Hydraulic |
| |
Application
fields
|
• Automatic dispensers
• Tablet testing
• Pipette control
• Dynamic or fast weighing
• Crystal growing machines
• Ashing and residue analysis
• Tensionmetry
• Thermogravimetry |
| |













